Cloud Storage: 7 Powerful Benefits You Can’t Ignore
In today’s fast-paced digital world, cloud storage has become a game-changer for individuals and businesses alike. It offers unmatched convenience, scalability, and security—transforming how we save, access, and share data from anywhere in the world.
What Is Cloud Storage and How Does It Work?

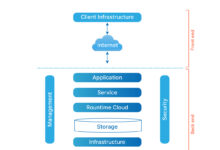
Cloud storage is a revolutionary technology that allows users to store data on remote servers accessed via the internet. Instead of saving files on a local hard drive or physical device, data is uploaded to data centers managed by cloud service providers. These centers are highly secure, redundant, and optimized for performance, ensuring your files are always available when needed.
Understanding the Core Mechanism
At its core, cloud storage relies on a network of interconnected servers distributed across multiple geographic locations. When you upload a file—be it a photo, document, or video—it’s broken into smaller chunks, encrypted, and stored across different servers. This process, known as data replication, ensures redundancy and high availability. Even if one server fails, your data remains intact and accessible from another location.
Data is encrypted both in transit and at rest for maximum security.Providers use advanced load-balancing techniques to distribute data efficiently.Users access their files through web interfaces or dedicated apps on various devices.”Cloud storage decouples data from physical hardware, enabling unprecedented flexibility and resilience.” — TechTargetTypes of Cloud Storage ModelsThere are three primary models of cloud storage: public, private, and hybrid.Public cloud storage, offered by companies like Google and Amazon, is hosted on shared infrastructure and is cost-effective for most users..
Private cloud storage is dedicated to a single organization, offering greater control and enhanced security—ideal for enterprises with strict compliance needs.Hybrid models combine both, allowing organizations to store sensitive data privately while leveraging public clouds for scalability..
Each model serves different needs. For example, startups often begin with public cloud solutions due to low entry costs, while financial institutions may opt for private or hybrid setups to meet regulatory standards like GDPR or HIPAA.
Top 7 Advantages of Cloud Storage
The shift to cloud storage isn’t just a trend—it’s a strategic move driven by tangible benefits. From cost savings to disaster recovery, the advantages are compelling and wide-ranging. Let’s explore the seven most powerful reasons why millions trust cloud storage every day.
1. Cost Efficiency and Reduced IT Overhead
One of the biggest draws of cloud storage is its cost-effectiveness. Traditional data storage requires significant investment in physical hardware, maintenance, cooling systems, and IT staff. With cloud storage, these burdens are eliminated. You pay only for the storage you use, often on a subscription basis, which makes budgeting predictable and scalable.
- No upfront capital expenditure on servers or data centers.
- Automatic scaling means you’re not paying for unused capacity.
- Providers handle maintenance, updates, and security patches.
According to a report by Gartner, businesses that migrate to the cloud can reduce IT infrastructure costs by up to 30%. This makes cloud storage especially attractive for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) looking to compete with larger players without the same financial resources.
2. Accessibility and Remote Work Enablement
In an era where remote work is increasingly common, cloud storage shines by enabling seamless access to files from any location, on any device. Whether you’re working from home, traveling, or collaborating across time zones, your data is just a login away.
- Files can be accessed via web browsers, mobile apps, or desktop sync tools.
- Real-time collaboration is possible with tools like Google Docs or Microsoft OneDrive.
- Team members can view, edit, and comment on shared documents simultaneously.
This level of accessibility has transformed workplace dynamics. A study by Microsoft found that 70% of remote workers feel more productive when using cloud-based tools, citing faster access to information and smoother collaboration as key factors.
3. Scalability and Flexibility
Unlike physical storage, which requires purchasing new hardware when capacity runs out, cloud storage scales instantly. Need more space? Upgrade your plan with a few clicks. Experiencing lower usage? Downgrade to save money. This elasticity is crucial for businesses with fluctuating data needs.
- Startups can begin with minimal storage and grow as their user base expands.
- Seasonal businesses (e.g., e-commerce during holidays) can scale up temporarily.
- Developers can test applications with large datasets without investing in local infrastructure.
Providers like Amazon S3 offer virtually unlimited storage, making it possible to store petabytes of data without worrying about physical limitations. This flexibility empowers innovation and reduces time-to-market for new products and services.
4. Enhanced Data Security and Compliance
Contrary to popular belief, cloud storage is often more secure than traditional on-premise solutions. Leading providers invest heavily in cybersecurity, employing encryption, multi-factor authentication, intrusion detection systems, and regular audits to protect user data.
- End-to-end encryption ensures only authorized users can access files.
- Automatic backups prevent data loss due to human error or malware.
- Compliance with standards like ISO 27001, SOC 2, and GDPR is standard practice.
For example, Google Cloud uses zero-trust security models and advanced AI to detect threats in real time. This level of protection would be prohibitively expensive for most organizations to implement independently.
5. Automatic Backup and Disaster Recovery
Data loss can be catastrophic—whether due to hardware failure, cyberattacks, or natural disasters. Cloud storage provides robust backup and disaster recovery solutions that minimize downtime and ensure business continuity.
- Files are automatically backed up in real time or at scheduled intervals.
- Geographic redundancy ensures data survives regional outages.
- Disaster recovery plans can be tested and executed quickly.
According to IBM, companies using cloud-based disaster recovery reduce recovery time by 60% compared to traditional methods. This resilience is vital for maintaining customer trust and operational stability.
6. Environmental Sustainability
Cloud storage contributes to environmental sustainability by optimizing resource usage. Data centers run at higher efficiency than individual on-premise servers, reducing energy consumption and carbon emissions.
- Providers use renewable energy sources like wind and solar power.
- Server virtualization maximizes hardware utilization.
- Cooling innovations (e.g., liquid cooling, AI-driven climate control) reduce energy waste.
For instance, Google has been carbon-neutral since 2007 and aims to run all its data centers on 24/7 carbon-free energy by 2030. By leveraging cloud storage, businesses indirectly support greener computing practices.
7. Integration with Modern Applications and AI
Cloud storage isn’t just a passive repository—it’s a dynamic platform that integrates with modern software ecosystems. From AI-powered analytics to machine learning models, cloud storage enables advanced data processing and automation.
- AI tools can analyze stored data to extract insights (e.g., customer behavior patterns).
- Automated workflows trigger actions based on file changes (e.g., invoice processing).
- APIs allow seamless integration with CRM, ERP, and collaboration tools.
For example, Microsoft Azure Blob Storage integrates with Azure Machine Learning to train models on large datasets stored in the cloud. This synergy between storage and intelligence is driving digital transformation across industries.
Popular Cloud Storage Providers in 2024
The market for cloud storage is highly competitive, with several major players offering diverse features, pricing models, and target audiences. Choosing the right provider depends on your specific needs—whether it’s personal file syncing, enterprise-grade security, or developer-friendly APIs.
Google Drive
Google Drive is one of the most widely used cloud storage platforms, especially among individuals and educational institutions. Integrated seamlessly with Google Workspace (Gmail, Docs, Sheets), it offers 15 GB of free storage and intuitive collaboration tools.
- Real-time co-editing of documents, spreadsheets, and presentations.
- Powerful search functionality powered by Google’s AI.
- Available on Android, iOS, Windows, and macOS.
For businesses, Google Workspace plans provide enhanced admin controls, unlimited storage (for enterprise tiers), and advanced security features. Its ease of use and deep integration with productivity apps make it a top choice for teams focused on collaboration.
Dropbox
Dropbox pioneered consumer cloud storage and remains a favorite for its simplicity and reliability. Known for its clean interface and robust syncing capabilities, Dropbox excels in file sharing and cross-device access.
- Smart Sync allows users to access files without taking up local disk space.
- File recovery options include version history up to 180 days (longer with extended plans).
- Dropbox Paper offers collaborative workspace for notes and project planning.
While Dropbox’s free tier is limited to 2 GB, its professional and business plans offer advanced features like e-signatures, admin dashboards, and integration with tools like Slack and Zoom. It’s particularly popular among creative professionals and remote teams.
Microsoft OneDrive
OneDrive is tightly integrated with the Microsoft ecosystem, making it ideal for users invested in Windows and Microsoft 365. It offers seamless file access across devices and powerful collaboration through Office apps.
- Files can be edited offline and synced automatically when back online.
- Personal Vault feature adds extra security with biometric or two-factor authentication.
- Business plans include compliance tools and data loss prevention (DLP).
OneDrive’s strength lies in its synergy with Outlook, Teams, and SharePoint. For enterprises using Microsoft 365, it provides a unified experience for document management and team collaboration.
Amazon S3 and AWS Storage Services
Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) is a cornerstone of Amazon Web Services (AWS), catering primarily to developers and enterprises. It offers high durability, scalability, and a wide range of storage classes for different use cases.
- S3 Standard for frequently accessed data.
- S3 Glacier for long-term archival with low retrieval frequency.
- Versioning, lifecycle policies, and cross-region replication enhance data management.
AWS also provides specialized services like EBS (Elastic Block Store) for virtual machines and S3 Intelligent-Tiering, which automatically moves data between storage classes based on usage patterns. While more complex than consumer-focused platforms, AWS offers unparalleled flexibility for large-scale applications.
Security Concerns and Best Practices for Cloud Storage
Despite its many benefits, cloud storage raises valid security concerns. Data breaches, unauthorized access, and compliance risks are real challenges that users must address proactively. However, with the right practices, cloud storage can be safer than traditional methods.
Common Security Risks
One of the biggest misconceptions is that cloud storage is inherently unsafe. In reality, most breaches occur due to human error, not provider vulnerabilities. Common risks include weak passwords, phishing attacks, misconfigured permissions, and unsecured devices.
- Shared links with unrestricted access can expose sensitive files.
- Lost or stolen devices with logged-in cloud accounts pose a threat.
- Insider threats—employees with excessive access rights—can misuse data.
A report by Verizon’s 2023 Data Breach Investigations Report found that 74% of breaches involved the human element, underscoring the importance of user education and policy enforcement.
Best Practices for Securing Your Data
To maximize security, users should adopt a layered approach. Start with strong authentication: use long, unique passwords and enable two-factor authentication (2FA). Regularly review access permissions and revoke access for former employees or unused apps.
- Encrypt sensitive files before uploading (client-side encryption).
- Use audit logs to monitor file access and detect anomalies.
- Train employees on phishing awareness and secure sharing practices.
“Security is not a product, but a process.” — Bruce Schneier, Security Expert
Additionally, choose providers that offer transparency reports, regular security audits, and compliance certifications. For businesses, implementing a Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB) can provide visibility and control over cloud usage across the organization.
Cloud Storage vs. Local Storage: A Comparative Analysis
The debate between cloud storage and local (on-premise) storage continues, especially as both technologies evolve. Each has strengths and weaknesses, and the best choice depends on specific use cases, budget, and risk tolerance.
Performance and Speed
Local storage typically offers faster data access because it doesn’t rely on internet connectivity. Reading and writing files to a local SSD or HDD is nearly instantaneous, making it ideal for high-performance tasks like video editing or large database operations.
- No latency from network transmission.
- Not affected by bandwidth limitations or ISP throttling.
- Better for real-time applications requiring low response times.
However, cloud storage performance has improved significantly with faster internet speeds and edge computing. Providers now use content delivery networks (CDNs) to cache data closer to users, reducing latency. For most everyday tasks—document editing, file sharing, backups—cloud performance is more than sufficient.
Cost Comparison Over Time
While local storage may seem cheaper upfront, long-term costs can add up. Initial hardware purchases are just the beginning. Ongoing expenses include maintenance, power, cooling, software licenses, and IT labor.
- Cloud storage follows an operational expenditure (OpEx) model.
- Local storage requires capital expenditure (CapEx) and depreciation planning.
- Cloud costs scale with usage; local costs are fixed regardless of utilization.
A total cost of ownership (TCO) analysis often reveals that cloud storage becomes more economical over time, especially for growing organizations. A study by Flexera’s 2023 State of the Cloud Report found that 58% of enterprises cite cost optimization as a primary driver for cloud adoption.
Data Control and Ownership
With local storage, organizations have full control over their data—where it’s stored, who accesses it, and how it’s protected. This level of control is crucial for industries with strict regulatory requirements, such as healthcare and finance.
- No reliance on third-party providers for data availability.
- Easier to conduct internal audits and ensure compliance.
- Can implement custom security policies and encryption standards.
Cloud storage, while highly secure, involves entrusting data to a third party. However, reputable providers offer detailed service level agreements (SLAs), data processing agreements (DPAs), and compliance frameworks to reassure customers. The key is choosing a provider that aligns with your regulatory and governance needs.
Future Trends in Cloud Storage Technology
Cloud storage is not static—it’s evolving rapidly in response to technological advancements and changing user demands. Emerging trends like edge computing, AI-driven optimization, and decentralized storage are reshaping the landscape.
Edge Computing and Distributed Storage
As the Internet of Things (IoT) expands, the need for low-latency data processing grows. Edge computing brings computation and storage closer to the data source, reducing reliance on centralized cloud servers.
- Sensors, cameras, and industrial machines process data locally before sending summaries to the cloud.
- Reduces bandwidth usage and improves response times.
- Enhances privacy by minimizing data transmission.
Companies like AWS (with Outposts) and Microsoft (Azure Edge Zones) are extending their cloud capabilities to the edge, creating hybrid architectures that combine the best of both worlds.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
AI is transforming cloud storage from a passive repository into an intelligent data management system. Machine learning algorithms can predict usage patterns, optimize storage tiers, detect anomalies, and even suggest file organization.
- Automated tagging and categorization of files based on content.
- Predictive analytics for storage capacity planning.
- AI-powered threat detection identifies suspicious access patterns.
For example, Google’s AI can automatically organize your photos by people, places, and events. In enterprise settings, AI helps reduce storage costs by identifying and archiving stale data.
Decentralized and Blockchain-Based Storage
An emerging alternative to traditional cloud storage is decentralized storage, which uses blockchain technology to distribute data across a peer-to-peer network. Platforms like Filecoin and Storj offer censorship-resistant, tamper-proof storage with economic incentives for node operators.
- Data is encrypted and split across multiple nodes globally.
- Users pay in cryptocurrency for storage services.
- No single point of failure or control.
While still in early adoption, decentralized storage promises greater privacy and resilience, especially for applications requiring high trust and transparency.
How to Choose the Right Cloud Storage Solution
With so many options available, selecting the right cloud storage provider can be overwhelming. The decision should be based on a clear understanding of your needs, budget, and long-term goals.
Assess Your Storage Needs
Start by evaluating how much data you need to store, how frequently it’s accessed, and who needs access. Personal users may prioritize ease of use and free tiers, while businesses must consider collaboration features, compliance, and scalability.
- Estimate current and projected storage requirements.
- Determine whether you need real-time sync or archival capabilities.
- Identify the types of files (documents, media, databases) you’ll store.
For example, a photographer may need high-capacity storage with fast upload speeds, while a legal firm may prioritize security and audit trails.
Evaluate Security and Compliance Features
Security should be a top priority. Look for providers that offer end-to-end encryption, two-factor authentication, and compliance with relevant regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA).
- Check if the provider allows client-side encryption.
- Review their data retention and deletion policies.
- Ensure they provide transparency about data centers and jurisdiction.
For regulated industries, choose providers with certifications like ISO 27001, SOC 2, or FedRAMP authorization.
Compare Pricing and Scalability
Pricing models vary widely. Some providers charge per user, others per gigabyte, and some offer tiered plans with bundled features. Be sure to understand all potential costs, including overage fees, egress charges, and API usage fees.
- Compare free tiers and trial periods.
- Look for transparent, predictable pricing with no hidden fees.
- Ensure the provider allows easy upgrades or downgrades.
For instance, AWS S3 has a complex pricing structure with different costs for storage, requests, and data transfer. In contrast, Dropbox offers simpler, flat-rate plans that may be easier to manage for small teams.
What is cloud storage?
Cloud storage is a service that allows users to save data on remote servers accessed via the internet. It enables file storage, backup, sharing, and access from any device with an internet connection, offering benefits like scalability, security, and cost efficiency.
Is cloud storage safe?
Yes, cloud storage is generally safe, especially when using reputable providers like Google, Microsoft, or Amazon. These companies employ advanced encryption, multi-factor authentication, and compliance measures to protect data. However, users should also follow best practices like using strong passwords and enabling 2FA.
How much does cloud storage cost?
Costs vary by provider and plan. Many services offer free tiers (e.g., Google Drive with 15 GB). Paid plans typically range from $2 to $10 per user per month for personal or small business use, while enterprise solutions can cost more based on storage volume and features.
Can I access cloud storage offline?
Yes, many cloud storage services allow offline access by syncing files to your device. For example, OneDrive and Dropbox let you mark files for offline use, so they remain available even without an internet connection. Changes sync once you’re back online.
What happens if the cloud provider goes out of business?
Reputable providers have exit strategies and data portability options. They typically give users ample notice and tools to download their data. To minimize risk, regularly back up critical data to another location and avoid vendor lock-in by using open formats.
Cloud storage has revolutionized the way we manage digital information. From empowering remote work to enabling AI-driven insights, its benefits are vast and growing. While challenges like security and cost management exist, the advantages far outweigh the drawbacks for most users. By understanding the different models, providers, and best practices, individuals and organizations can make informed decisions that enhance productivity, security, and scalability. As technology evolves, cloud storage will continue to play a central role in our digital lives—offering a powerful, flexible, and sustainable solution for the future of data.
Further Reading: